Recently I had the advantage of attending one of the virtual sessions with Health Canada at the Livable Virtual Conference Canada, focused on wellness and accessibility in the design industry. The virtual session was about the education of radon and creating an awareness strategy for Canadians on radon risk and encouraging actions to reduce those risks.
What is radon?
Naturally occurring radioactive gas.
Radon is produced from the breakdown of uranium which is found in soil and rocks across the country.
It is colourless, tasteless and odourless.
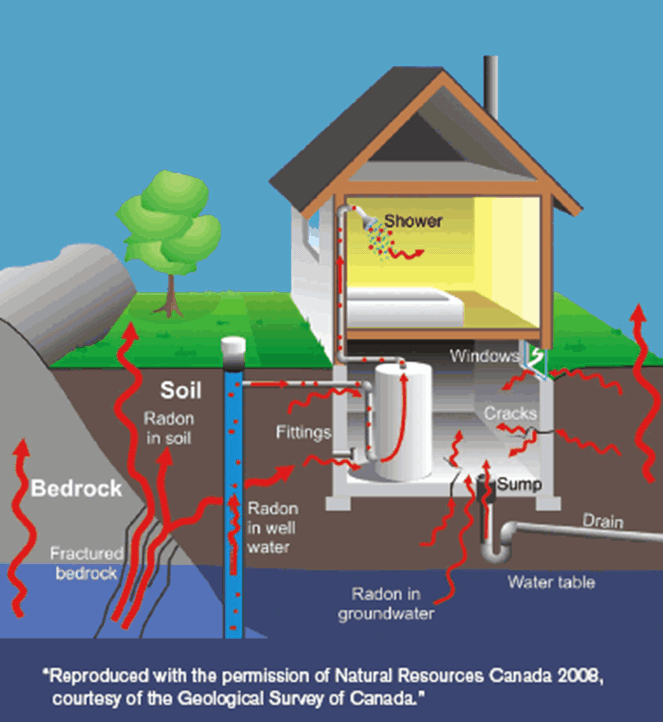
Image courtesy- Health Canada
Where is radon found and how can it enter your home?
Radon enters the atmosphere by moving through the pores in the soil. In outdoor air, radon levels are low as it dilutes when it comes in contact with air. But indoor radon levels can vary. The current Canadian guideline for Radon is 200 Bq/m3.
It can enter the home through a sump pump, through cracks in the foundation, between construction joints as well as through well water. Radon is soluble in water and when you turn on a tap that Radon can off-gas the air that you breathe.
Why is radon bad for our health?
Radon is the largest source of natural radiation exposure.
Radon is the number one leading cause of lung cancer for non-smokers.
Testing your home for Radon
Options for radon testing
Hire a certified radon measurement professional.
Purchase a certified long term, do-it-yourself Kit by the Canadian national radon proficiency program.
In-person: Retail hardware stores.
Online: takeactionradon.ca/test
Things to consider when purchasing a radon test kit.
Ideals time to start testing for Radon is during the fall and winter because your windows are closed and you see a high accumulation operated on at this time.
Purchase a long-term radon detector (91 days or longer because radon level fluctuates and you might get false results.
Radon detector should be certified by (C-NRPP)
Place the radon test kit where you spend most of your time and make sure it remains for the 91 days period and after that period of time, package it up and send it to the laboratory.
Image courtesy-Health Canada
How to reduce the radon level in your home
Radon levels in your house can be lowered by hiring a certified professional to install a mitigation system.
Increase ventilation in the house.
Fix or seal radon entry points.
The most common mitigation system is called an active soil depressurize pressurization system.
A pipe is installed through the foundation floor slab. The pipe is attached to a fan that continuously runs to draw the radon from beneath the floor slab and vents the raid directly outside.
If you need more information on radon, you can go to canada.ca/radon.
A certified list of vendors can be found on takeactiononradon.ca
Want some Interior Design Inspirations and need to be on top of the latest design trends. Here are some blog posts you might like to read…